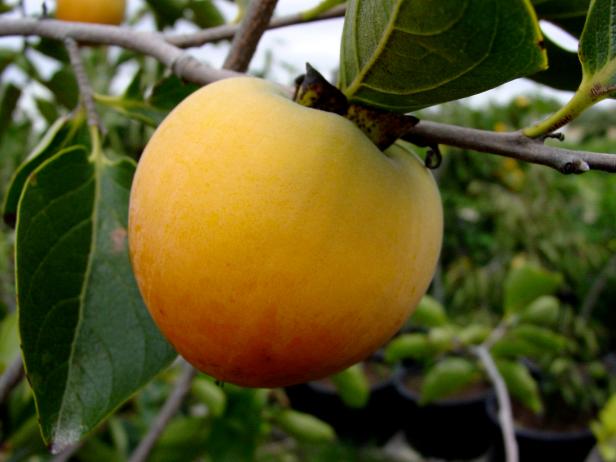
Persimmons can make lots of dishes taste better. They’re good to eat whether fresh, dried, or cooked, making them a great thing to add to meals.
Table of Contents
- Sending Persimmons from Japan to Other Places
- Summary
- Japanese Persimmons in Food
- Sending Persimmons from Japan to Other Places
- Summary
- Japanese Persimmons in Food
- Sending Persimmons from Japan to Other Places
- Summary
- Japan’s National Fruit
- The Story of the Japanese Persimmon
- Persimmons in Japanese Culture
- 1. Cooking:
- 2. Good Luck and More:
- 3. Parties and Festivities:
- 4. Art and Creativity:
- Growing and Picking Persimmons
- Japanese Persimmons in Food
- Sending Persimmons from Japan to Other Places
- Summary
Sending Persimmons from Japan to Other Places
Persimmons from Japan are liked all over the world, and Japan sends a lot of them to other countries.
Here’s what’s important to know about their export:
- Main Buyers: The big places that buy these persimmons are the United States, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Singapore. There are other buyers too, like Canada, China, and South Korea.
- Varieties: Japan sells different kinds of persimmons like Fuyu, Hachiya, and Jiro. Each type has its own special flavor and texture.
- Picking and Shipping: They pick persimmons mainly in the fall, from September to December. They keep them in cold storage until they’re ready to send them. They have to be very careful when moving them so they don’t get damaged.
- Rules for Selling: There are strict rules for sending persimmons to other countries. They must be checked for pests and diseases. Some countries also have rules about bringing in fresh fruit that can affect how many persimmons they buy from Japan.
- Money Matters: Selling persimmons is a big deal in Japan. It makes a lot of money every year and gives jobs to people who work on farms and with crops.
Selling their persimmons is an important way for Japan to do business with other countries. They need to make sure the persimmons are top quality and that they follow all trade rules so that the fruit gets to people fresh and ready to enjoy.
Summary
The Japanese persimmon is really important in the food and culture of Japan. It has a rich history and many people there grow it and love it today.
This fruit is also sent to many places around the world. With its sweet taste and ability to be used in different recipes, the Japanese persimmon is a unique fruit that adds something special to any table.
- Pollination: Some Japanese persimmon trees can pollinate themselves, but many others need another tree’s pollen to produce fruit. This is where bees and different insects are very important for pollination.
- Growing Fruit: After pollination, fruits start to grow on the trees. When it’s fall, and they look colorful and feel firm, the Japanese persimmons are ready to pick.
- Picking Fruit: People usually pick Japanese persimmons by hand, using small cutting tools and climbing ladders. They carefully cut the fruit off and gently place it into baskets or boxes.
- Keeping Them Fresh: Persimmons can be kept for quite a while in a cool and dry spot. It’s important to handle them gently so they don’t get bruised or hurt. Some types, like the hachiya persimmons, need to ripen before you can eat them, but others, like fuyu persimmons, are good to eat even when hard.
Growing and picking Japanese persimmons takes careful work and understanding how the trees grow. If done right, you can get a lot of tasty and healthy fruit.
Japanese Persimmons in Food
Japanese persimmons are great for many kinds of dishes, both sweet and not sweet. Here’s how people often use them in cooking:
- Hoshigaki: This is a special treat in Japan where people dry persimmons in the sun. They become sweet and chewy, and are great for eating on their own or in baked goodies.
- Persimmon Sushi: There’s a kind of sushi with persimmon in it, along with rice, pickled veggies, and sometimes fish. The sweet and sour flavor of the persimmon is really tasty with the other parts of the sushi.
- Salads: Persimmon can make salads taste sweeter and juicier. This is especially true when you put them with greens that are more bitter. They also make fruit salads more colorful because of their bright orange color.
- Sweet Treats: Persimmons are popular for desserts where their sweetness and softness are perfect. Some examples are persimmon pies, cakes, and puddings.
- Drinks: They can add flavor to drinks like tea, juices, and even some alcoholic drinks. One famous drink in Japan uses persimmons soaked in sake.
Persimmons can make lots of dishes taste better. They’re good to eat whether fresh, dried, or cooked, making them a great thing to add to meals.
Sending Persimmons from Japan to Other Places
Persimmons from Japan are liked all over the world, and Japan sends a lot of them to other countries.
Here’s what’s important to know about their export:
- Main Buyers: The big places that buy these persimmons are the United States, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Singapore. There are other buyers too, like Canada, China, and South Korea.
- Varieties: Japan sells different kinds of persimmons like Fuyu, Hachiya, and Jiro. Each type has its own special flavor and texture.
- Picking and Shipping: They pick persimmons mainly in the fall, from September to December. They keep them in cold storage until they’re ready to send them. They have to be very careful when moving them so they don’t get damaged.
- Rules for Selling: There are strict rules for sending persimmons to other countries. They must be checked for pests and diseases. Some countries also have rules about bringing in fresh fruit that can affect how many persimmons they buy from Japan.
- Money Matters: Selling persimmons is a big deal in Japan. It makes a lot of money every year and gives jobs to people who work on farms and with crops.
Selling their persimmons is an important way for Japan to do business with other countries. They need to make sure the persimmons are top quality and that they follow all trade rules so that the fruit gets to people fresh and ready to enjoy.
Summary
The Japanese persimmon is really important in the food and culture of Japan. It has a rich history and many people there grow it and love it today.
This fruit is also sent to many places around the world. With its sweet taste and ability to be used in different recipes, the Japanese persimmon is a unique fruit that adds something special to any table.
- Planting: They plant persimmon trees from small ones or by putting branches onto an existing tree’s roots. Trees like lots of sunshine and good soil and are planted in neat rows. It can take a few years before they start making fruit.
- Trimming: Growers cut the trees to shape them and make them produce more fruit. This is usually done when the trees are not growing, in the winter.
- Pollination: Some kinds of persimmons make fruit on their own,
- Pollination: Some Japanese persimmon trees can pollinate themselves, but many others need another tree’s pollen to produce fruit. This is where bees and different insects are very important for pollination.
- Growing Fruit: After pollination, fruits start to grow on the trees. When it’s fall, and they look colorful and feel firm, the Japanese persimmons are ready to pick.
- Picking Fruit: People usually pick Japanese persimmons by hand, using small cutting tools and climbing ladders. They carefully cut the fruit off and gently place it into baskets or boxes.
- Keeping Them Fresh: Persimmons can be kept for quite a while in a cool and dry spot. It’s important to handle them gently so they don’t get bruised or hurt. Some types, like the hachiya persimmons, need to ripen before you can eat them, but others, like fuyu persimmons, are good to eat even when hard.
Growing and picking Japanese persimmons takes careful work and understanding how the trees grow. If done right, you can get a lot of tasty and healthy fruit.
Japanese Persimmons in Food
Japanese persimmons are great for many kinds of dishes, both sweet and not sweet. Here’s how people often use them in cooking:
- Hoshigaki: This is a special treat in Japan where people dry persimmons in the sun. They become sweet and chewy, and are great for eating on their own or in baked goodies.
- Persimmon Sushi: There’s a kind of sushi with persimmon in it, along with rice, pickled veggies, and sometimes fish. The sweet and sour flavor of the persimmon is really tasty with the other parts of the sushi.
- Salads: Persimmon can make salads taste sweeter and juicier. This is especially true when you put them with greens that are more bitter. They also make fruit salads more colorful because of their bright orange color.
- Sweet Treats: Persimmons are popular for desserts where their sweetness and softness are perfect. Some examples are persimmon pies, cakes, and puddings.
- Drinks: They can add flavor to drinks like tea, juices, and even some alcoholic drinks. One famous drink in Japan uses persimmons soaked in sake.
Persimmons can make lots of dishes taste better. They’re good to eat whether fresh, dried, or cooked, making them a great thing to add to meals.
Sending Persimmons from Japan to Other Places
Persimmons from Japan are liked all over the world, and Japan sends a lot of them to other countries.
Here’s what’s important to know about their export:
Advertisements- Main Buyers: The big places that buy these persimmons are the United States, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Singapore. There are other buyers too, like Canada, China, and South Korea.
- Varieties: Japan sells different kinds of persimmons like Fuyu, Hachiya, and Jiro. Each type has its own special flavor and texture.
- Picking and Shipping: They pick persimmons mainly in the fall, from September to December. They keep them in cold storage until they’re ready to send them. They have to be very careful when moving them so they don’t get damaged.
- Rules for Selling: There are strict rules for sending persimmons to other countries. They must be checked for pests and diseases. Some countries also have rules about bringing in fresh fruit that can affect how many persimmons they buy from Japan.
- Money Matters: Selling persimmons is a big deal in Japan. It makes a lot of money every year and gives jobs to people who work on farms and with crops.
Selling their persimmons is an important way for Japan to do business with other countries. They need to make sure the persimmons are top quality and that they follow all trade rules so that the fruit gets to people fresh and ready to enjoy.
Summary
The Japanese persimmon is really important in the food and culture of Japan. It has a rich history and many people there grow it and love it today.
This fruit is also sent to many places around the world. With its sweet taste and ability to be used in different recipes, the Japanese persimmon is a unique fruit that adds something special to any table.
Japan is a country known for its deep cultural roots and traditions. People all over the world are intrigued by Japanese culture, especially their food which is famous for its fine flavors and beautiful look.
Out of all the tasty foods in Japan, there is a special fruit that reflects Japan’s culture and farming history. It’s called the “kaki” in Japanese or the Japanese persimmon. Let’s learn why this fruit is so important and why it became Japan’s national fruit.
AdvertisementsJapan’s National Fruit
The kaki, or Japanese persimmon, is Japan’s national fruit. It has been part of the Japanese diet for many, many years. It’s important to Japanese food and culture, and people use it in both sweet and savory recipes.
Native to Japan and other parts of East Asia, the Japanese persimmon comes from the same family as the ebony tree. It is valued for its distinct taste, softness, and health perks.
This fruit can be round or oval and has shiny, smooth skin, which can be light yellow-orange to dark reddish-orange, depending on the type. Its flesh is juicy and sweet but can sometimes taste a bit tangy.
There are mostly two kinds of Japanese persimmons: ones that make your mouth feel dry (astringent) and ones that don’t (non-astringent). Non-astringent persimmons are more popular in Japan and other countries. They are full of good stuff like fiber, vitamins A and C, and potassium. They are a favorite snack or dessert and used in traditional Japanese meals.
The Story of the Japanese Persimmon
Japanese persimmons have a fascinating history in Japan. People think they first came from China over 2,000 years ago and came to Japan in the 8th century. At first, people grew them because they looked pretty, with their bright color and interesting shape, decorating gardens and temples.
AdvertisementsHowever, it wasn’t until the Edo period (1603-1868) that people started eating them. Farmers began to grow more persimmon trees, and people made lots of traditional dishes with persimmons, like hoshigaki (dried sweet persimmons), which people in Japan still love.
Later, during the Meiji period (1868-1912), a new kind of persimmon called the “fuyu” was developed. It was less tangy and could be eaten when it was still quite firm, leading to more ways of enjoying persimmons.
Even today, Japanese persimmons are a big deal in Japan, part of its cultural identity. They show up in many modern and classic recipes and get shipped to other countries too. They are celebrated in cultural events and festivals year-round, representing Japan’s traits and heritage.
Persimmons in Japanese Culture
In Japanese life, the persimmon is big. It has a unique taste, a neat look, and means a lot symbolically.
Here’s what makes persimmons special in Japan:
Advertisements1. Cooking:
Japanese people love using persimmons in their recipes. There’s hoshigaki, persimmon sushi, sweet persimmon mochi, and persimmon salad, making them a key part of Japanese food tradition.
2. Good Luck and More:
Persimmons are linked to luck, success, and a long life in Japan. Their sunny color reminds people of the sun and the seasons. Giving persimmons as gifts in the New Year is a way to wish for happiness and success.
3. Parties and Festivities:
They’re central to lots of Japanese festivals. Every fall, places all over Japan have persimmon festivals with special foods, games, and a chance to learn about persimmons and their place in Japan.
4. Art and Creativity:
Persimmons influence Japanese art and creations. Artists use the fruit’s shape and color in their work. Its image is popular in fabrics and pottery designs too.
Persimmons aren’t just a fruit in Japan; they tell stories of the country’s long past and deep customs.
AdvertisementsGrowing and Picking Persimmons
People typically grow persimmons in special orchards and gather them from September to December, which can change based on the weather and the type of persimmon.
Here’s how they grow and harvest persimmons:
- Planting: They plant persimmon trees from small ones or by putting branches onto an existing tree’s roots. Trees like lots of sunshine and good soil and are planted in neat rows. It can take a few years before they start making fruit.
- Trimming: Growers cut the trees to shape them and make them produce more fruit. This is usually done when the trees are not growing, in the winter.
- Pollination: Some kinds of persimmons make fruit on their own,
- Pollination: Some Japanese persimmon trees can pollinate themselves, but many others need another tree’s pollen to produce fruit. This is where bees and different insects are very important for pollination.
- Growing Fruit: After pollination, fruits start to grow on the trees. When it’s fall, and they look colorful and feel firm, the Japanese persimmons are ready to pick.
- Picking Fruit: People usually pick Japanese persimmons by hand, using small cutting tools and climbing ladders. They carefully cut the fruit off and gently place it into baskets or boxes.
- Keeping Them Fresh: Persimmons can be kept for quite a while in a cool and dry spot. It’s important to handle them gently so they don’t get bruised or hurt. Some types, like the hachiya persimmons, need to ripen before you can eat them, but others, like fuyu persimmons, are good to eat even when hard.
Growing and picking Japanese persimmons takes careful work and understanding how the trees grow. If done right, you can get a lot of tasty and healthy fruit.
Japanese Persimmons in Food
Japanese persimmons are great for many kinds of dishes, both sweet and not sweet. Here’s how people often use them in cooking:
- Hoshigaki: This is a special treat in Japan where people dry persimmons in the sun. They become sweet and chewy, and are great for eating on their own or in baked goodies.
- Persimmon Sushi: There’s a kind of sushi with persimmon in it, along with rice, pickled veggies, and sometimes fish. The sweet and sour flavor of the persimmon is really tasty with the other parts of the sushi.
- Salads: Persimmon can make salads taste sweeter and juicier. This is especially true when you put them with greens that are more bitter. They also make fruit salads more colorful because of their bright orange color.
- Sweet Treats: Persimmons are popular for desserts where their sweetness and softness are perfect. Some examples are persimmon pies, cakes, and puddings.
- Drinks: They can add flavor to drinks like tea, juices, and even some alcoholic drinks. One famous drink in Japan uses persimmons soaked in sake.
Persimmons can make lots of dishes taste better. They’re good to eat whether fresh, dried, or cooked, making them a great thing to add to meals.
AdvertisementsSending Persimmons from Japan to Other Places
Persimmons from Japan are liked all over the world, and Japan sends a lot of them to other countries.
Here’s what’s important to know about their export:
- Main Buyers: The big places that buy these persimmons are the United States, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Singapore. There are other buyers too, like Canada, China, and South Korea.
- Varieties: Japan sells different kinds of persimmons like Fuyu, Hachiya, and Jiro. Each type has its own special flavor and texture.
- Picking and Shipping: They pick persimmons mainly in the fall, from September to December. They keep them in cold storage until they’re ready to send them. They have to be very careful when moving them so they don’t get damaged.
- Rules for Selling: There are strict rules for sending persimmons to other countries. They must be checked for pests and diseases. Some countries also have rules about bringing in fresh fruit that can affect how many persimmons they buy from Japan.
- Money Matters: Selling persimmons is a big deal in Japan. It makes a lot of money every year and gives jobs to people who work on farms and with crops.
Selling their persimmons is an important way for Japan to do business with other countries. They need to make sure the persimmons are top quality and that they follow all trade rules so that the fruit gets to people fresh and ready to enjoy.
Summary
The Japanese persimmon is really important in the food and culture of Japan. It has a rich history and many people there grow it and love it today.
This fruit is also sent to many places around the world. With its sweet taste and ability to be used in different recipes, the Japanese persimmon is a unique fruit that adds something special to any table.
Advertisements